Flat springs
Contents |
Introduction
Flat springs are flat strips of material which, when deflected by an external load, store and release energy. These types of spring are small, stamped metal components that function like a spring by controlling deflection within small or restricted spaces.
Manufactured from high carbon spring steel, nickel-silver, high nickel alloys and stainless steel, a flat spring can function as a spacer or ground.
Applications
Flat springs come in a range of different shapes and sizes for various applications. They are used for numerous purposes within differing industries, such as motors, office equipment, generators, counterbalances, doors and electrical switchgear.
There are many different types of flat spring including the leaf spring and flat coil spring.
Leaf Spring
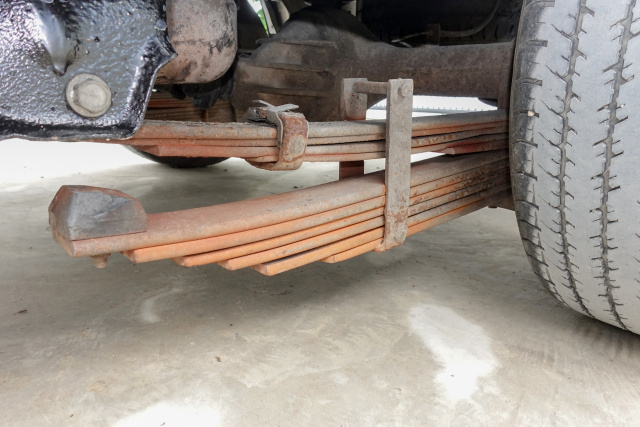
Leaf springs are one of the oldest forms of spring, dating back to medieval times, they are an important component in suspension, such as in cars or other vehicles. They provide stability and help minimise wear and tear on other parts.
Created with individual layers or leaves of metal, they are often used in automotive design on drive or steer axles. Constructed of high alloy spring steel or lighter weight materials such as low carbon steel, this type of spring comes in three basic types; mono-leaf springs, multi-leaf springs and parabolic springs.
Mono-Leaf Spring
A mono-leaf spring consists of one plate of springs which is thick in the centre and tapers out to the ends. The amount and length of the taper is critical to the durability and safety of the spring. This type of spring provides lesser spring rates that can hold up a vehicle, also offering less stiffness in terms of bending and controlling the axle.
Multi-Leaf Spring
A multi-leaf spring is an engineered system designed to provide support, stability and safety to a vehicle. The length and make-up of each spring is important as each leaf is designed to carry a proportionate amount of load and stress. Each leaf is designed to provide support to the leaf above and below it, and it is this feature which provides support for the vehicle.
Parabolic Spring
A parabolic spring is a leaf or set of leaves which are tapered in a parabolic form rather than in a linear one. The tapering in a single leaf handles the force distribution from the vehicle to the axle, and works as a complete multi-leaf spring. Parabolic springs design is characterised by fewer leaves the thickness of which varies from the centre to ends following a parabolic curve, preventing unwanted inter-leaf friction. They tend to have more flexibility and are commonly used on buses.
Flat Coil Springs
Flat coil springs are used with a counterweight to control the action of valves, such as those in a vehicle exhaust system. They are wound into a specific configuration to absorb shocks or provide tension, and can be found in seating to provide support, or in automotive applications.
--European Springs and Pressings Ltd 12:46, 15 Nov 2017 (BST)
Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Compression springs.
- Key qualities of springs.
- Mechanical engineer.
- Spring materials.
- Tension springs v torsion springs.
- Torsion springs and their benefits.
- Using springs in construction to prevent disaster.
- Spotlight On: Flat Springs
- Spotlight on Compression Springs
- The Difference Between Tension and Torsion Springs
- The Importance of Gas Springs
- The Multiple Uses of Compression Springs
- The Uses of Wire Forms Within the Construction Industry
- Types of spring.
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
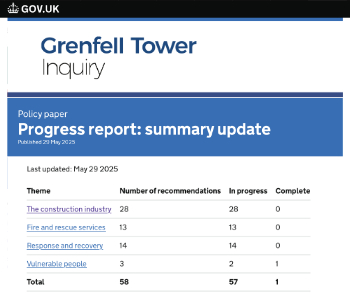
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.